Bing Is #4, State of Digital Agencies, AI and Copyright

Local: Bing in Fourth Place
Monday we published a preliminary analysis of Apple Maps traffic vs. Google for local search/discovery. Mike's conclusion was that roughly 37% of iPhone owners are using Apple Maps for directions and that Apple is generating about 5% of the local site visits and 10% of the calls driven by Google. Map Labs did a similar but broader analysis comparing traffic from Google, Bing, Apple and Yelp to 100 business locations in the hospitality industry. We found that 28% of Apple Maps lookups are category searches; Map Labs had a similar number: 30%. But Map Labs determined that Apple was responsible for 50% of the directions requests of Google Maps (on the iPhone). Still, Google drives 9x the calls and 10x the web visits of Apple Maps. Most surprising perhaps is Bing's comparative weakness in local. Map Labs found Bing was in fourth place, after Apple and Yelp, way behind Google. The full analysis with much more discussion and detail is available here.
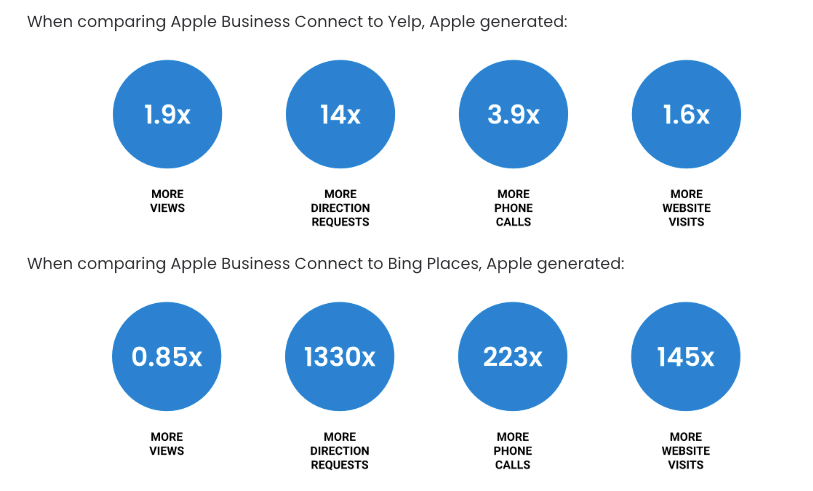
Our take:
- Most local SEOs are focused on Google, of course, and then Bing. Some also focus on Yelp. However that should be revised in light of these findings.
- While Bing is driving local traffic and actions, its relative importance is much lower than the common perception.
- By comparison, Apple is often neglected. It's the clear number two in local search now.
Websites Most Profitable for Agencies
Near Media and UpCity recently conducted a digital agency survey. It's unpublished, but we hope to present some of that data soon. In the meantime, Vendasta has produced a similar study (lead form), based on a survey of 400 North American digital agencies. The largest cohort had fewer than 10 employees. Roughly 50% have been in business 6+ years; 56% are making under $1 million annually. In fact, 36% are pulling in <$150K, though another 36% are making $1 - $3 million. Average revenue per client for most of the $1 million+ club is $50K or more. But agencies with higher revenue also had higher churn. Agencies making over $1 million are more heavily committed to AI, though 69% say they're new to it. Websites are the most profitable offering, while ads is the least profitable. SEO is in the middle. Nearly two-thirds (62%) of agencies said they were seeking to reduce or consolidate their tech stacks. Most have few sales reps (<5) and say their most effective channel is WoM.
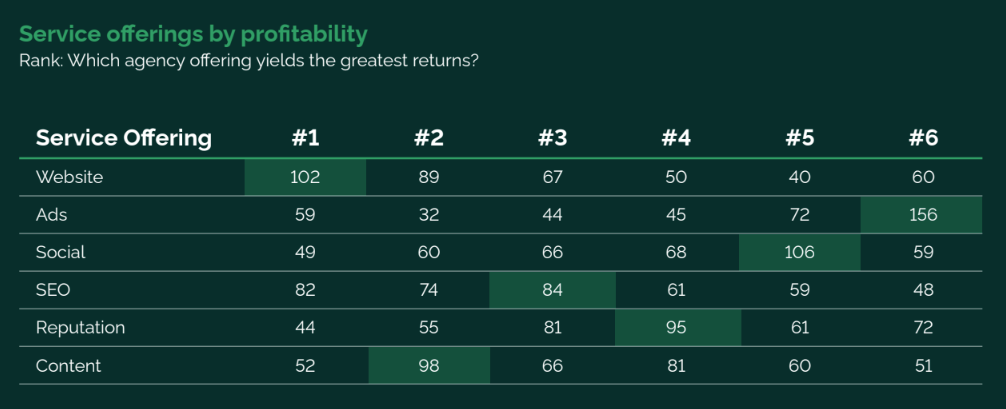
Our take:
- The top two challenges faced by agencies are "scaling services and operations" and "balancing new business development with existing client work."
- Number of clients in most cases is correlated with staffing, although 22% of agencies under 10 employees managed 100+ accounts.
- In the NM-UpCity survey, SEO was most profitable and was perceived by roughly equal sized groups as easy and difficult to implement/fulfill.
AI, Scraping and Copyright
OpenAI, Meta and Google are all being sued (e.g., here, here) for scraping content for AI training data sets. There are multiple other lawsuits pending as well. For example, Getty Images can show examples of its mangled Getty logo in AI-generated images. That's a smoking gun, but in other cases it may be much harder to prove specific works were ingested by LLMs. Yet, effectively, the entire web corpus is being used to train AIs. On the one hand, massive copyright infringement is implied by the sheer breadth of scraping. But a federal appeals court ruled that web scraping of public data is legal (hiQ Labs, Inc. v. LinkedIn Corp.). The same case also said, however, that scraping in violation of a site's terms is not protected. In response, some sites (e.g., Twitter, Reddit, Stack Overflow) are starting to charge for their data. And OpenAI has entered into agreements with AP and Shutterstock to license data for future AI training. But there's a big difference between scraping for search indexes and AI training; LLMs aren't delivering traffic back to publishers.

Our take:
- All publishers must assume that their content is being scraped for LLMs. OpenAI will allow robots.txt for those that want to block scraping. Per hiQ Labs, publishers can also block scraping in their terms.
- There will be more lawsuits. But the emerging model is data licensing. Smaller publishers and individuals, however, will probably not benefit.
- Courts will face a dilemma in terms of infringement proof thresholds and determining compensation. Managing permissions/payments will be challenging and expensive for AI platforms unless they limit training data.
Short Takes
- Using local SEO to do site selection for brick and mortar locations.
- Old, but: duplicate reviews on LSAs and GBP could lead to suspension.
- Google, Microsoft compete to bring AI to $4T healthcare market (WSJ).
- Workers doing mid-level writing boosted productivity with ChatGPT.
- FTC investigating whether ChatGPT caused any "consumer harm."
- Why the recent "social media communication" ruling is flawed (NYT).
- Twitter claims "99.99%" of tweets are "healthy content," others say no.
- Uber, DoorDash, Grubhub fight to block driver wage increases in NYC.
- Tax firms sent sensitive customer data to Meta without permission.
- Delaware becomes 12th state to introduce big data privacy law.
- Prime Day sales up 6.1%, fall short of analysts' estimates of 10%.
Listen to our latest podcast.

How can we make this better? Email us with suggestions and recommendations.

